Introduction to Immunopathology
Definition:- Immunopathology is a branch of medicine that deals with immune responses associated with the disease. It includes the study of the pathology of an organism, organ system, or disease with respect to the immune system, immunity, and immune responses.
Types of immunity: two broad categories:-
1.Innate immunity
2.Adaptive immunity
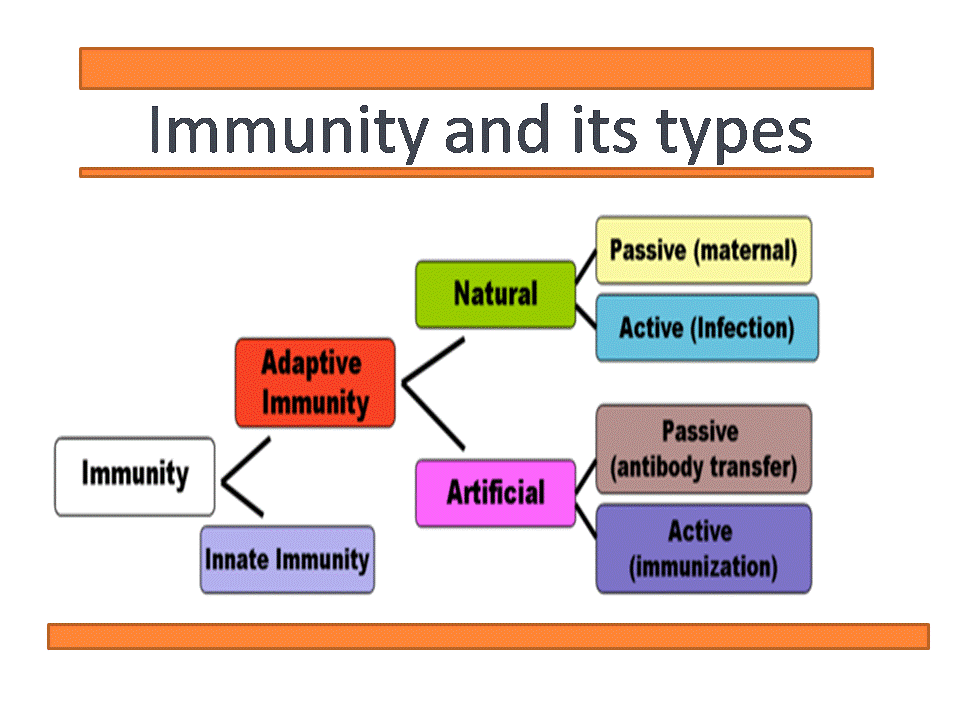
Innate immunity:
- also called natural, or native immunity.
- is the first line of defense.
- The major components of innate immunity are:
- Epithelial barriers that block entry of environmental
- microbes.
- Phagocytic cells (mainly neutrophils and macrophages).
- Natural killer (NK) cells.
- Plasma proteins including the proteins of the complement system.
Adaptive immunity:
- also called acquired, or specific immunity.
- develops later after exposure to microbes.
- also capable of recognizing non-microbial substances called antigens.
- Adaptive immunity is more powerful in combating infections.
- Two main types of adaptive immunity:
Cell-mediated ( cellular ) immunity:
Responsible for defense against intracellular microbes ( viruses and T.B ). This is mediated by T- lymphocytes.
Humoral immunity:
protects against extracellular microbes and their toxins ( Bacteria ). mediated by B - lymphocytes which differentiate into antibody-secreting cells called plasma cells and their secreted products called antibodies : ( IgM, IgD, IgG, IgA, and IgE ).
Thanks & Regards
Vikas Tiwari


Comments
Post a Comment